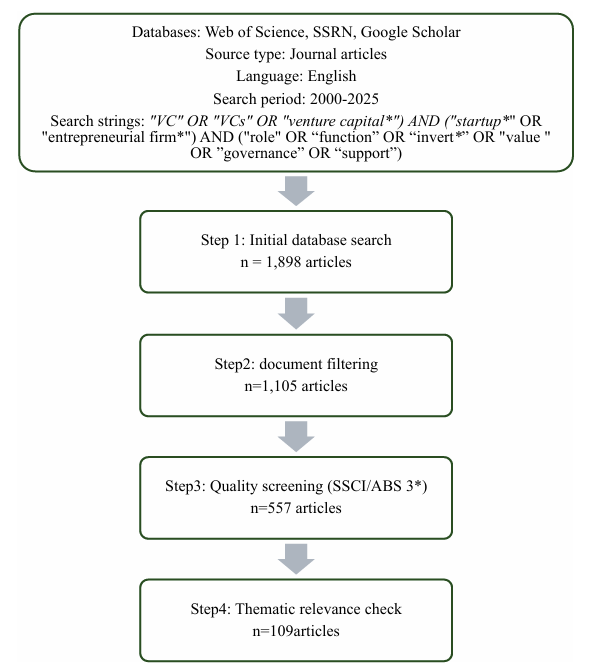
Despite the recognized importance of venture capital (VC) in fostering entrepreneurship, its functional evolution remains inadequately conceptualized in existing literature. This paper conducts a systematic review of 109 studies published from 2000 to 2025 and explores the dynamic trajectory of VC in entrepreneurship lifecycle. Moving beyond the traditional view of VC as a mere financial intermediary, we propose a multi-dimensional framework that captures its expanded functions of resource orchestration, strategic partnership, and cognitive collaboration. Our findings indicate that the manifestation of these roles is not uniform, but varies systematically with the type of investor, the timing of their engagement, and the broader institutional setting. By developing a dynamic model of VC functionality, this review provides a nuanced understanding of how VC’s role deepens over time and offers critical insights for entrepreneurs and investors to enhance the efficacy of VC-firm partnerships.